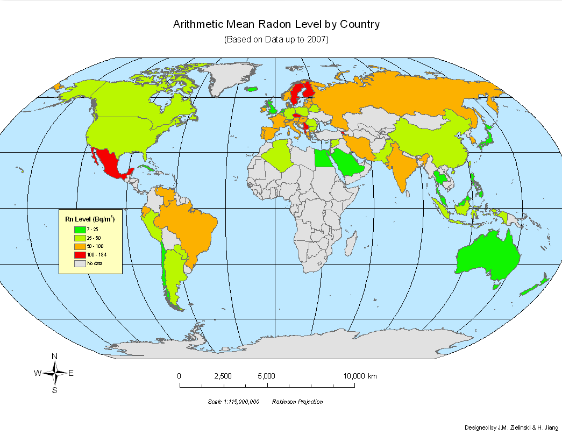
Radon Levels worldwide
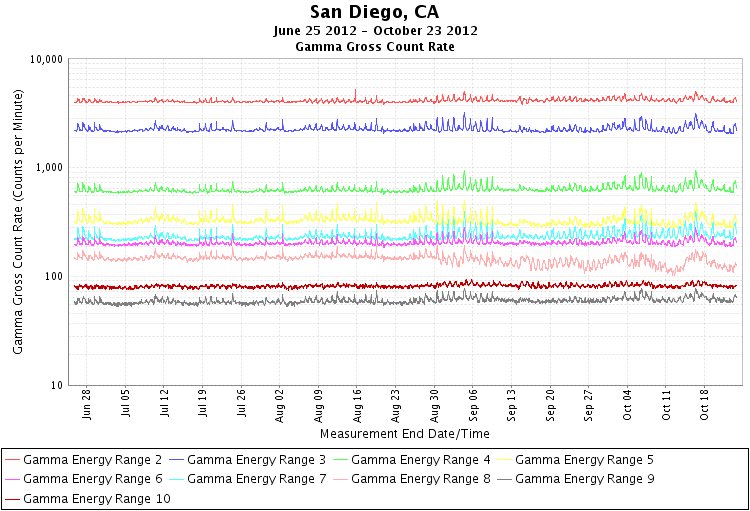
San Diego Gamma Ray
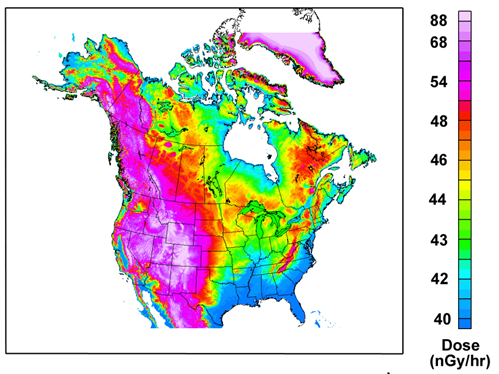
Cosmic Ray Exposure
EPA's RadNet map
This page is under construction. Ultimately it will provide an introduction to Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing radiation
Radiation refers to the movement of energetic particles or waves. Ionizing radiation refers to radiation that is capable of delivering enough energy to a molecule that the molecule becomes charged (or ionized). Ionizing radiation typically proceeds by “knocking” one or more electrons, positrons, or protons out of an atom or molecule. When a molecule or atom loses an electron (or other charged sub-atomic particle) it no longer has equal numbers of positive and negative charges and carries a net charge itself. Charged or non-neutral atoms or molecules are called ions. Due to their net charge ions tend to be more reactive than neutral atoms or molecules. When molecules inside of living cells are ionized biological functions can be compromised. Genetic damage accumulates over lifetime exposure to ionizing radiation, thus biological systems suffer both short term and a long term cumulative damage from exposure to ionizing radiation.
Types of ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation can come in the form of a high energy electromagnetic wave or a subatomic particle. Electromagnetic (EM) radiation with photonic energies greater than 10 electron volts (or wavelengths shorter than 125 nm) are classified as ionizing. This region of the EM spectrum includes the deep ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, and gamma rays. (1)
A variety of subatomic particles can
Electrons, positrons, protons, muons, and
Neutrons
The types of radiation most commonly seen are alpha, beta, gamma
Sources of Ionizing radiation
Both types of ionizing radiation can be emitted from a nuclear decay. In a nuclear reaction… The types of radiation most commonly seen are alpha, beta, gamma
Nuclear reaction and decay processes
Unstable nuclei,
Decay chain; ex radon; named alpha, beta, gamma: Rutherford spotlight “he made a case for an international ban on the use of aeroplanes in warfare.”
Background radiation sources:
Cosmic, primordial, terrestrial,







